

- #Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate how to
- #Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate software
- #Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate code
In other words, the typical value of a PK/PD parameter is the value of PK/PD parameter with η=0. Where θ CL is the typical value and η CL is the corresponding inter-subject variability following normal distribution with mean zero and covariance, e.g., Ω 11. For example, systemic clearance is expressed as The typical PK/PD of the population is summarized by θ, and individual PK/PD parameters are expressed as a combination of θ and η. The function f1 represents a structural model describing the relationship between the PK/PD observations and the model parameter θ, while η and ε represent the stochastic model components describing the randomness unexplained by the structural model. Θ, Ω, and Σ are constants while η and ε are random variables.
Ε~MVN (0, Σ): intra-individual (i.e., residual) random variability modeled using multivariate normal distribution with mean zero and covariance matrix Σ Η~MVN (0, Ω): inter-individual random variability modeled using multivariate normal (MVN) distribution with mean zero and covariance matrix Ω (or intra-individual) variability parameter (ε). Y=f 2(F, ε): the observation (Y) given by F and the residual The following notations are used for PK/PD modeling using NONMEM®:į=f 1(θ, η, χ): the model predicted (i.e., fitted) value (F), model parameter (θ), interindividual random variability parameter (η), and covariates (χ) defining structural model to explain pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics Lastly, the discussion section concludes with a few remarks and conclusions. In the results section, the numerical results are summarized and compared. Then detailed explanations on the three methods, including the suggested simple method of obtaining the covariance matrix of EBE in NONMEM® VI using verbatim code, are provided. In the methods section, theoretical backgrounds for calculation of the EBE and the standard errors of EBE are overviewed along with the descriptions on the four models and the two datasets used to assess the different ways of calculating the standard of errors of EBE. The contents of this paper are as follows.
#Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate how to
The objectives of this study are to illustrate how to directly obtain the SE of EBE by the use of NONMEM® VI internal matrix POSTV and to evaluate the performance by comparing the results with other methods. phi file, one of the new output files from NONMEM® 7. However, the elements of the POSTV matrix are available as ETC columns in the. The POSTV matrix is not available in the new version of NONMEM® 7, either. Unfortunately, this feature is not available in the previous versions of NONMEM®. However, a more direct method to obtain the SE of EBE is possible with NONMEM® VI using one of the internal variables, POSTV. A Perl based automated utility to calculate the SE of EBE is available in PsN® version 2.2.6 or later.
#Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate code
Writing one's own code requires careful thinking and programming expertise. Therefore postprocessing after a modeling NONMEM run is necessary to obtain the SE of EBE. The SE of EBE of the inter-subject variability parameter η is not available in the output file of NONMEM®. Also the SE of EBE can be used for simulation considering the uncertainty in the inter-subject variability. The SE of EBE is an enhanced model diagnosis tool to assess the precision of the estimated inter-subject variability parameter η.
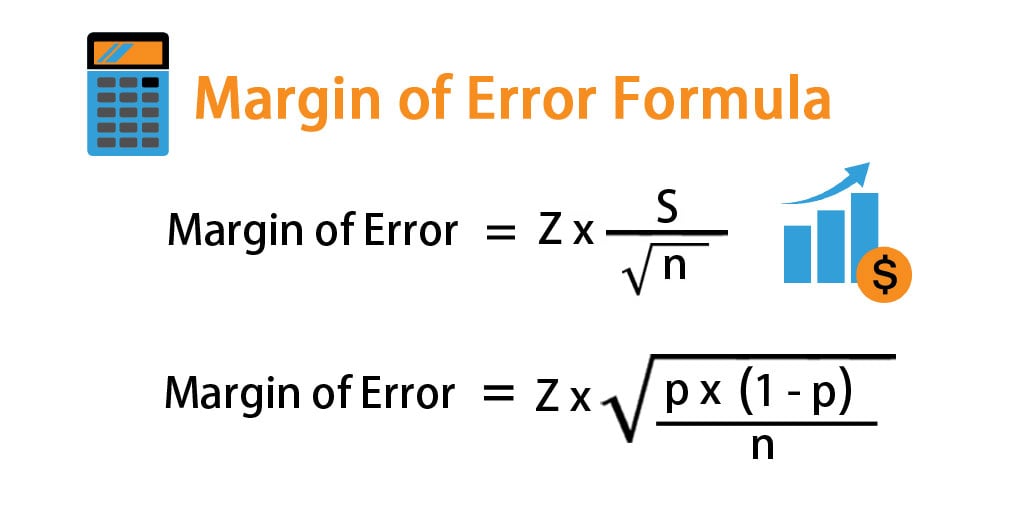
However the standard error (SE) of the empirical Bayes estimate (EBE) of the inter-subject variability parameter η is not provided in the NONMEM® output file. NONMEM® uses inter-subject variability parameter η to describe the individual differences in PK/PD parameters.
#Shortcut method to calculate standard error estimate software
NONMEM® (NONlinear Mixed Effects Model) is the most widely used software for the population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling and simulation, also is the standard tool for drug development as well as regulatory approval.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
